When it comes to rice, the battle between brown rice and white rice has been ongoing for quite some time. People often wonder which variety is healthier and more nutritious. In this article, we will delve into the nutritional differences, health benefits, and potential drawbacks of both brown rice and white rice. So, grab a bowl of rice and let’s explore the age-old question: Which is healthier, brown rice or white rice?
Brown Rice: The Nutritional Powerhouse
Brown rice, the unrefined version of white rice, is often hailed as a nutritional powerhouse due to its higher fiber and nutrient content. Let’s take a closer look at the health benefits of brown rice.
1. Fiber: Promoting Digestive Health
Brown rice is an excellent source of dietary fiber, which is vital for maintaining a healthy digestive system. Fiber aids in promoting regular bowel movements, preventing constipation, and reducing the risk of digestive disorders.
2. Vitamins and Minerals: A Treasure Trove of Nutrients
Compared to white rice, brown rice is rich in vitamins and minerals. It contains significant amounts of B vitamins, including thiamin, niacin, and vitamin B6, which play crucial roles in energy production, brain function, and overall well-being. Additionally, brown rice is a good source of magnesium, selenium, and manganese.
3. Antioxidants: Protecting against Free Radicals
Brown rice is packed with antioxidants that help combat free radicals in the body. These antioxidants, such as phenolic compounds and flavonoids, have been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease and certain types of cancer.
White Rice: The Refined Classic
White rice, the more commonly consumed variety, undergoes a refining process that removes the bran and germ layers, resulting in a polished appearance and altered nutritional profile. Let’s examine the characteristics of white rice and its potential impact on health.
1. Refined Grain: Reduced Fiber Content
One significant difference between white rice and brown rice is the fiber content. During the refining process, the outer bran and germ layers are removed, diminishing the fiber content in white rice. As a result, it may not provide the same digestive benefits as its brown counterpart.
2. Enriched with Nutrients: A Fortified Option
To compensate for the loss of natural nutrients during refinement, white rice is often fortified with essential vitamins and minerals. This enrichment process adds back certain nutrients, such as iron and B vitamins, to the refined grains. While this improves the nutritional profile, it still falls short compared to the naturally occurring nutrients in brown rice.
3. Easier Digestibility: A Gentle Option
White rice is often preferred by individuals with sensitive stomachs or digestive issues due to its easier digestibility. The removal of the bran and germ layers makes white rice less likely to cause digestive discomfort or irritation, making it a gentler option for some.
Which is Healthier: Brown Rice or White Rice?
Now that we have explored the nutritional aspects of both brown rice and white rice, let’s address the burning question: Which is healthier, brown rice or white rice?
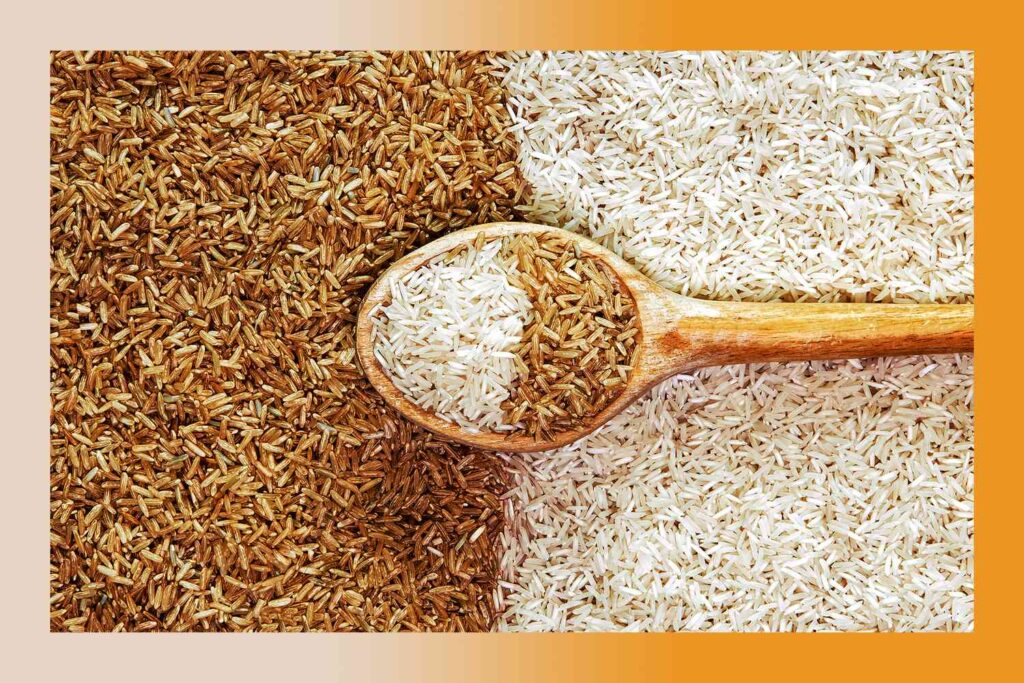

It’s important to note that the term “healthier” can vary depending on individual health goals and dietary needs. However, in general, brown rice tends to be considered the healthier option due to its higher fiber and nutrient content. The presence of fiber aids in digestion, helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels, and promotes a feeling of fullness, which can support weight management. Additionally, the higher vitamin and mineral content in brown rice provides added nutritional value.
However, it’s essential to consider individual circumstances and preferences. For individuals with certain digestive issues or specific dietary requirements, white rice may be a more suitable choice. Its gentler digestibility and enriched nutrient profile can be beneficial in such cases. It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the best option based on personal needs.
In the battle of brown rice vs. white rice, the winner ultimately depends on individual health goals and preferences. Brown rice shines with its higher fiber and nutrient content, promoting digestive health and providing a range of vitamins and minerals. On the other hand, white rice offers easier digestibility and can be suitable for individuals with sensitive stomachs or specific dietary needs.
Both varieties have their merits, and incorporating a variety of grains into your diet can provide a well-rounded nutritional profile. Remember to prioritize portion control, balance, and overall dietary diversity to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
So, whether you choose the nutty and fiber-rich brown rice or the gentler and refined white rice, enjoy your meal mindfully and savor the goodness that each variety brings to the table!
Read Our Blogs – Click here for More Blogs
FAQs
Yes, brown rice generally takes longer to cook than white rice. The outer bran layer in brown rice requires more time to soften and absorb water, resulting in a longer cooking time. However, with modern cooking techniques like using a pressure cooker or rice cooker, the cooking time can be significantly reduced.
Brown rice and white rice have similar calorie content. The difference lies in their nutritional profiles. While brown rice contains more fiber and nutrients, it doesn’t necessarily mean it is higher in calories. Both varieties can be part of a balanced diet, with portion control being the key to managing calorie intake.
Yes, white rice can be a part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation. It provides a source of energy and can be included as part of a balanced meal with vegetables, protein, and healthy fats. However, it’s important to note that the refining process removes some of the natural nutrients found in brown rice.
Brown rice is often recommended for weight loss due to its higher fiber content, which promotes a feeling of fullness and can aid in weight management. The fiber in brown rice slows down digestion, helping to control appetite and prevent overeating. However, it’s important to consider overall calorie intake and portion sizes when focusing on weight loss goals.
If you’re considering switching from white rice to brown rice, it’s best to do it gradually. Abruptly changing your diet may cause digestive discomfort, as your body needs time to adjust to the higher fiber content of brown rice. Start by incorporating small amounts of brown rice into your meals and gradually increase the proportion over time.
Yes, mixing brown rice and white rice can be a way to enjoy the benefits of both varieties. This combination offers a compromise between the nutritional value of brown rice and the gentler digestibility of white rice. It allows you to obtain some additional nutrients while still enjoying the texture and taste of white rice.